Summary
This article explores the critical importance of OT-IT integration in achieving smart manufacturing success, highlighting how advanced technologies can transform operational efficiency. Key Points:
- Leverage semantic technologies for true interoperability between OT and IT systems, enabling complex event processing and proactive responses to anomalies.
- Utilize advanced AI/ML algorithms for anomaly detection that not only identify issues but also determine root causes, facilitating efficient corrective actions and minimizing downtime.
- Adopt digital twins combined with real-time data and AI to enhance predictive maintenance strategies, optimizing operations and asset lifespan.
Understanding OT-IT Integration in Industry 4.0
Picture a manufacturing facility where machines communicate seamlessly with one another and relay real-time data to a centralized system. This system then analyzes the information and delivers actionable insights aimed at enhancing operational efficiency. This scenario is not merely a concept from science fiction; it represents the tangible advancements of Industry 4.0, made feasible by integrating Operational Technology (OT) with Information Technology (IT).
In our current fast-paced industrial environment, merging OT and IT has evolved from being just a popular trend to an essential strategy for success. The process of OT-IT integration brings numerous benefits, including improved data interoperability and real-time analytics that empower organizations to make informed decisions quickly.
To facilitate this seamless connection between operational technology and information technology, various technologies have emerged as key players. For instance, edge computing allows data processing closer to the source—reducing latency while enhancing response times. Moreover, IoT devices play a crucial role in collecting and transmitting data efficiently.
Standards and protocols like OPC UA or MQTT are also vital in ensuring effective communication across systems, enabling robust data exchange between different platforms. These measures ensure that organizations can leverage their technological investments fully.
As we explore the journey of OT-IT integration further, it’s important to recognize both its challenges—such as cybersecurity risks—and best practices that can help mitigate these issues effectively. By examining case studies that illustrate successful integrations within various industries, we can better understand how theoretical concepts translate into practical applications that drive real change in today’s industrial landscape.
Challenges Faced by ABC Manufacturing Before Integration
At ABC Manufacturing, a medium-sized producer of automotive components, various challenges were evident prior to this integration effort. Their machinery operated largely in isolation, each equipped with its unique controls and data management systems. This lack of cohesive integration resulted in notable inefficiencies along with frequent machine downtimes that ultimately caused delays in production schedules. Moreover, outdated legacy systems hampered the ability to exchange data in real time. The absence of interoperability between OT and IT—often due to incompatible protocols like OPC UA or MQTT—further complicated matters.
Additionally, material limitations within their machinery made seamless integration difficult while gaps in workforce skills regarding advanced technologies hindered the transition toward more integrated solutions. These factors collectively contributed to the obstacles faced by ABC Manufacturing before they could successfully implement an effective OT-IT integration strategy.
| Key Considerations | Best Practices |
|---|---|
| Understanding Distinctions between OT and IT | Starting Out With A Well-Defined Strategy |
| Ensuring Effective Communication through Standardized Protocols | Leveraging Edge Computing Technologies for Local Processing |
| Addressing Security Issues with Robust Protection Mechanisms | Adopting Unified Platforms for Interoperability |
| Maintaining Data Integrity through Clear Governance Practices | Investing In Robust Cybersecurity Measures Against Threats |
| Fostering Collaboration Among Stakeholders to Align Goals | Planning For Scalability Upfront to Accommodate Growth |
How OT-IT Integration Solves Manufacturing Inefficiencies
By bridging the gap between OT and IT, ABC Manufacturing sought to realize several key benefits: improved operational efficiency through streamlined processes; predictive maintenance powered by sophisticated algorithms; enhanced smart manufacturing features; and better-informed decision-making based on real-time insights.
However, there were notable barriers hindering efficiency due to existing silos between OT and IT systems. These isolated pockets of information created obstacles for effective collaboration among teams, limiting their ability to work together efficiently. Ultimately, overcoming these silos is essential for leveraging the full potential of integrated technologies in modern manufacturing environments.
Real-Time Monitoring and Its Impact on Productivity
Why Integrating Operational Technology (OT) with Information Technology (IT) is Important: Consider Vinod and Sarah, who manage production at ABC Manufacturing. Each morning, they would spend hours walking around the factory floor just to check the status of every machine manually. This routine was not only time-consuming but also prone to inaccuracies.
By integrating OT with IT, we could streamline this process significantly. With IoT-enabled devices equipped with various sensors—like thermal imaging for equipment temperature monitoring—they could receive real-time updates on machine statuses directly on customizable dashboards. Utilizing communication methods such as MQTT or HTTP/2 would ensure that data transmission happens swiftly without delays.
Moreover, employing predictive maintenance algorithms can help anticipate potential issues before they occur, further enhancing efficiency in operations. A seamless flow of information allows for immediate decision-making based on accurate data gathered from machines constructed with diverse materials that might impact sensor precision.
This integration fosters a more efficient workflow by minimizing manual checks while enabling operators like Vinod and Sarah to focus on optimizing productivity rather than getting bogged down by tedious tasks.

 Free Images
Free ImagesThe Role of Predictive Maintenance in Reducing Downtime
On another note, Li Wei, who oversees maintenance, previously relied on routine maintenance schedules. However, despite his diligent efforts, unexpected machine breakdowns frequently occurred, resulting in costly downtimes. With the advent of predictive maintenance technologies—like machine learning algorithms that analyze historical performance data alongside current sensor inputs—Li Wei has begun transitioning away from purely scheduled fixes. High-quality materials used in sensors contribute significantly to their durability and accuracy for continuous monitoring.
Moreover, the integration of Internet of Things (IoT) devices allows for ongoing observation of equipment health. Advanced analytics software plays a crucial role by identifying patterns linked to potential equipment failures. This capability enables timely interventions before issues escalate into serious problems that could disrupt production lines further. Through these advancements, predictive maintenance effectively reduces downtime while promoting overall operational resilience.
Automating Production Adjustments with Smart Manufacturing
Improving Decision-Making Through Comprehensive Data Access
Overcoming Challenges in Integrating Diverse Systems
By integrating OT data from sensors and machinery with IT data from enterprise systems, organizations can achieve a much deeper understanding of their operations. Moreover, adopting standardized communication protocols like MQTT or OPC UA can greatly enhance interoperability between different systems. The utilization of rugged industrial devices designed to endure harsh environments further supports this integration process. Emphasizing modular architecture in system design also allows for smoother upgrades and the incorporation of new technologies over time. Ultimately, sharing real-world case studies that showcase successful integration solutions can offer practical insights and foster confidence in these strategies.
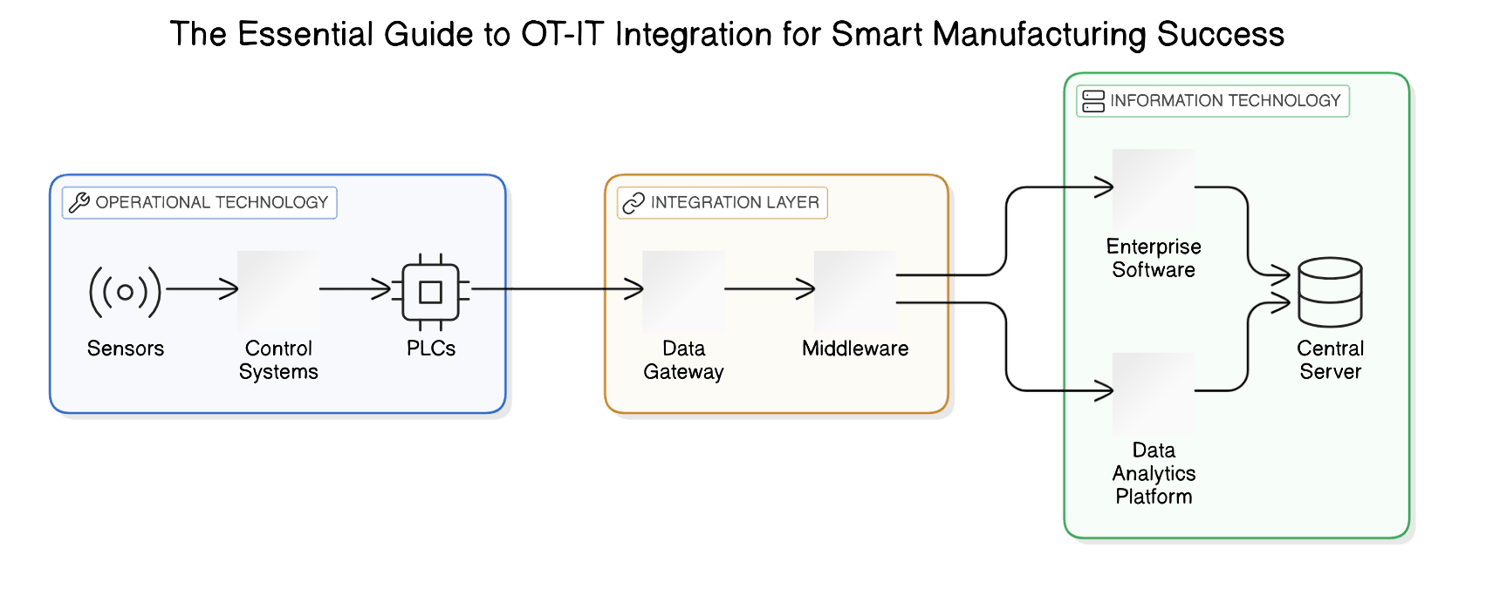
Key Considerations for Successful OT-IT Integration
Many industrial settings are characterized by this combination of old and new technologies. Legacy systems often rely on proprietary protocols that were never designed to interface with contemporary IT infrastructure, leading to significant integration hurdles. To navigate these complexities, it’s crucial to adopt data interoperability standards such as OPC UA which facilitate seamless communication between OT and IT systems. Moreover, implementing robust cybersecurity measures tailored specifically for protecting sensitive manufacturing information during integration processes cannot be overlooked.
The role of cloud computing also plays a pivotal part in scaling these integration efforts effectively. Additionally, investing in workforce training focused on both OT and IT systems can make the transition smoother while enhancing overall system performance significantly.
Best Practices to Maximize the Benefits of Integration
Afzal, who was in charge of cybersecurity, became aware that connecting OT systems with IT could expose them to various cyber threats. In response, she adopted strategies such as network segmentation, encryption practices, and regular security evaluations to safeguard the integrated systems. These actions ensured that both the factory's data and its operations remained secure from cyber attacks. Traditionally isolated from external networks, OT systems face increased cybersecurity risks when IIoT is introduced; therefore, implementing strong protective measures against potential cyber threats is a significant hurdle.
Michael highlighted how crucial it is to maintain high-quality and consistent data throughout the integrated environments. The team put in place data governance protocols aimed at ensuring that information sourced from OT systems was accurate, reliable, timely, and consistent. This focus allowed for dependable analysis and decision-making processes. Managing data quality across diverse OT frameworks is vital for successful integration; inconsistencies in data format or quality can lead to errors and inefficiencies within the system.
Initially operating separately within their own spheres without much interaction were ABC Manufacturing’s OT and IT departments. To bridge this gap effectively, Ravi along with Michael coordinated regular joint meetings alongside training sessions designed to enhance collaboration among teams. By aligning all stakeholders towards shared objectives through these efforts made the integration process considerably smoother.
The integration effort began modestly with a pilot project involving just a handful of machines; once it proved successful, ABC Manufacturing expanded this initiative across its entire plant while ensuring that their solution had enough flexibility built-in to accommodate future growth opportunities. Taking this phased approach allowed them time to refine their strategy further while addressing scalability concerns.
Key Considerations for Integrating Operational Technology with Information Technology include:
1. **Understanding Distinctions**: Recognizing that OT systems prioritize real-time control focused on reliability while IT solutions emphasize flexibility in business operations is essential.
2. **Ensuring Effective Communication**: Achieving seamless interoperability between OT and IT requires careful planning around standardized protocols or middleware solutions enabling smooth data exchange between disparate systems.
3. **Addressing Security Issues**: New security vulnerabilities emerge when merging these two domains; hence robust protection mechanisms—including network segmentation along with ongoing security assessments—are critical.
4. **Maintaining Data Integrity**: High-quality information forms an essential foundation for effective integrations; establishing clear governance practices ensures accurate representation across both sectors.
5.Fostering Collaboration Among Stakeholders: Successful integration hinges on teamwork among different departments—from operations through management—therefore aligning everyone behind common goals proves pivotal.
Best Practices for Successfully Merging Operational Technology With Information Technology involve:
1.Starting Out With A Well-Defined Strategy: Clearly outline your objectives along with creating a comprehensive plan detailing scope timelines plus necessary resources before embarking upon larger implementations—a pilot project may serve well here too!
2.Leveraging Edge Computing Technologies : Utilizing edge computing allows immediate local processing reducing latency while conserving bandwidth—which remains paramount especially where quick response times are concerned!
3.Adopting Unified Platforms : Seek out platforms capable of bridging gaps supporting both sides' functionalities—they should facilitate collection analysis & interoperability securely as well!
4.Investing In Robust Cybersecurity Measures : Your strategy must encompass thorough protections against hacking attempts including network isolation encryption access controls alongside routine audits assessing vulnerabilities
5.Planning For Scalability Upfront : Design your architecture anticipating growth so it accommodates evolving business demands featuring adaptable technologies capable handling future expansions seamlessly
6.Cultivating A Collaborative Atmosphere : Promoting teamwork amongst your operational technology & informational technology staff helps eliminate barriers improving communication driving innovation forward within smarter manufacturing initiatives!
Reference Articles
IT/OT Convergence - The Essential Guide
IT/OT Convergence is essentially a confluence of distributed computing power, data processing, and the OT systems that manage and control ...
Source: Industrial CyberIT/OT Convergence in Manufacturing: Steps to Achieve a ...
Explore a step-by-step guide on how to leverage IT/OT convergence in manufacturing to develop a smart factory.
Source: MatellioMaximizing Industrial IoT Potential with OT-IT Integration
Why It Matters: Learn how OT-IT integration drives business growth, operational efficiency, and competitive advantage.
Source: Medium · Prashanth Y PIT-OT Convergence Is a Requirement for Smart Manufacturing
Successful IT-OT integration is an essential step in the journey towards creating a fully connected, dynamic and flexible Smart Manufacturing enterprise. It's ...
The ultimate guide to industrial IoT for smart manufacturing
From real-time monitoring to predictive maintenance, IIoT illuminates the path toward a more connected, intelligent, and responsive manufacturing ecosystem.
Source: LinkedIn · Octopus DigitalWhat is IT/OT Convergence? Everything You Need to Know
IT/OT convergence is the integration of information technology systems with operational technology systems. IT systems are used for data-centric computing; ...
Source: TechTargetSmart Manufacturing Technology - Revolution in 2025 - Signify
Design an OT/IT Architecture : Ensure seamless integration of operational and information technologies. Launch MVPs: Start small with minimum ...
Source: getsignify.com


 ALL
ALL Precision Machinery
Precision Machinery
Related Discussions